Case Study: How Military Can Adopt MCP for Secure Data Integration Across Classification Levels
How military and intelligence organizations can securely enable AI copilots to fuse classified and unclassified data across multiple security domains using Model Context Protocol (MCP) — a standardized and governed approach to connect AI assistants with mission-critical systems.
1. Background
Modern defense operations rely on a vast range of intelligence inputs — HUMINT, SIGINT, GEOINT, and OSINT — each classified at varying levels. The challenge lies in enabling AI copilots to leverage this data safely without compromising classified sources or breaking cross-domain security rules.
- Problem: Intelligence and operational data exist across classification domains (UNCLASSIFIED → TOP SECRET), often siloed and hard to integrate.
- Goal: Allow AI copilots to securely access, summarize, and fuse intelligence from multiple sources while enforcing strict clearance and governance controls.
2. Challenges
- Cross-Domain Security: Integrating classified and unclassified systems without leakage.
- Access Control: Enforcing need-to-know and attribute-based permissions for AI-driven operations.
- Auditability: Maintaining complete traceability of AI interactions with sensitive systems.
- Operational Agility: Avoiding fragile, one-off integrations between AI tools and intelligence platforms.
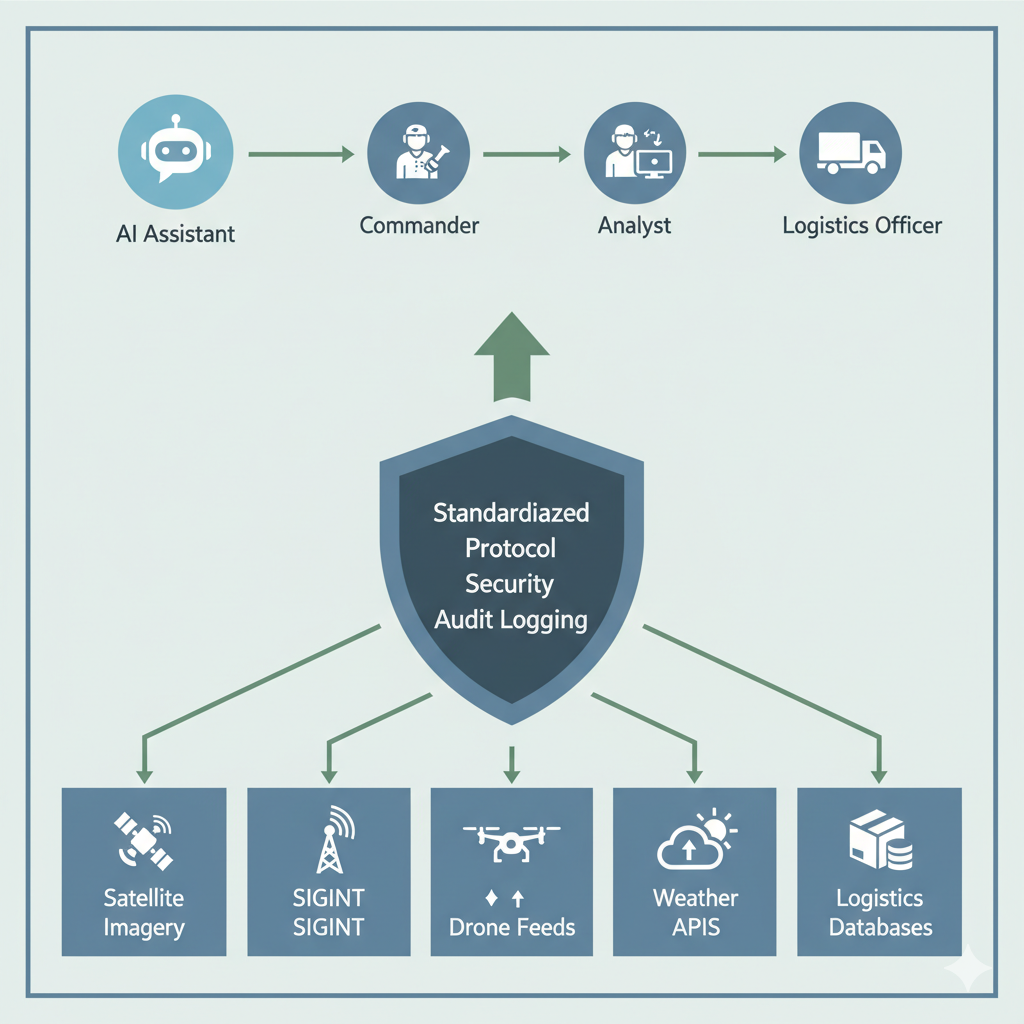
3. The Solution — Model Context Protocol (MCP)
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) establishes a secure, standardized interface between AI assistants and defense intelligence systems.
It ensures that every AI query, summary, and fusion operation adheres to classified data governance and military compliance frameworks.
MCP as a Secure Integration Layer
Instead of direct integrations, each intelligence API (e.g., from DCGS, ISR data lakes, or mission planning servers) is wrapped as an MCP tool.
These tools define precise input/output schemas, security scopes, and audit metadata.
Example MCP Tool Definitions:
| Tool Name | Description | Access Level |
|---|---|---|
getIntelReport(reportId) | Fetches a classified intelligence summary | SECRET+ |
analyzeOpenSource(query) | Correlates unclassified OSINT data | UNCLASSIFIED |
shareSecureData(recipient, dataId) | Distributes sanitized intelligence with redactions | Controlled Release |
4. Identifying High-Value Use Cases
1. Intelligence Analysis
Fuse HUMINT, SIGINT, and OSINT data streams to detect emerging threat networks — with outputs automatically redacted by clearance level.
2. Mission Planning
Combine terrain intelligence, meteorological data, and classified logistics to generate secure operational plans compliant with need-to-know access.
3. Cross-Domain Collaboration
Enable inter-agency or allied force collaboration through controlled redaction layers that ensure compliance within Multi-Level Security (MLS) frameworks.
4. Cyber Defense Operations
Leverage AI copilots that can correlate real-time threat feeds with classified incident logs to automate containment actions — without exposing sensitive data.
5. Security Architecture
The MCP layer embeds defense-grade controls:
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Tool invocations bound to clearance level and mission role.
- OAuth 2.0 & Cross-Domain Auth: Secure authentication across classified and unclassified domains.
- End-to-End Encryption: All API transactions encrypted with DoD-standard cryptography.
- Centralized Audit Logs: Every MCP call recorded for forensics and compliance review.
6. AI Copilot Integration
AI copilots interact with MCP tools to execute queries, fusions, and analyses — but never handle raw classified data directly.
Example Workflow:
User Prompt → “Fuse HUMINT with OSINT on insurgent activity in Region X.”
- The AI assistant calls MCP tool
getIntelReport()(classified) andanalyzeOpenSource()(unclassified). - MCP enforces access filters and fuses sanitized results.
- AI returns a redacted, contextually rich summary approved for the user’s clearance level.
This design preserves the AI’s analytical flexibility while maintaining ironclad data boundaries.
7. Governance & Compliance Framework
MCP provides inherent governance features critical for defense-grade AI deployments.
Key Capabilities
- Comprehensive Audit Trails: Every AI–system interaction logged with timestamp, clearance, and purpose.
- Data Minimization: Only mission-relevant fields exposed to copilots.
- Policy Enforcement: Compliance with DoD 5200.1-R, NIST SP 800-53, and MLS security models.
- Automated Redaction: Built-in sanitization rules ensure data shared across domains meets clearance protocols.
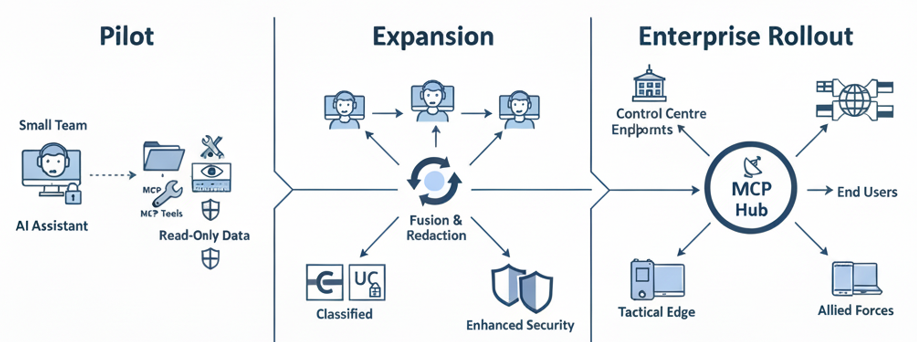
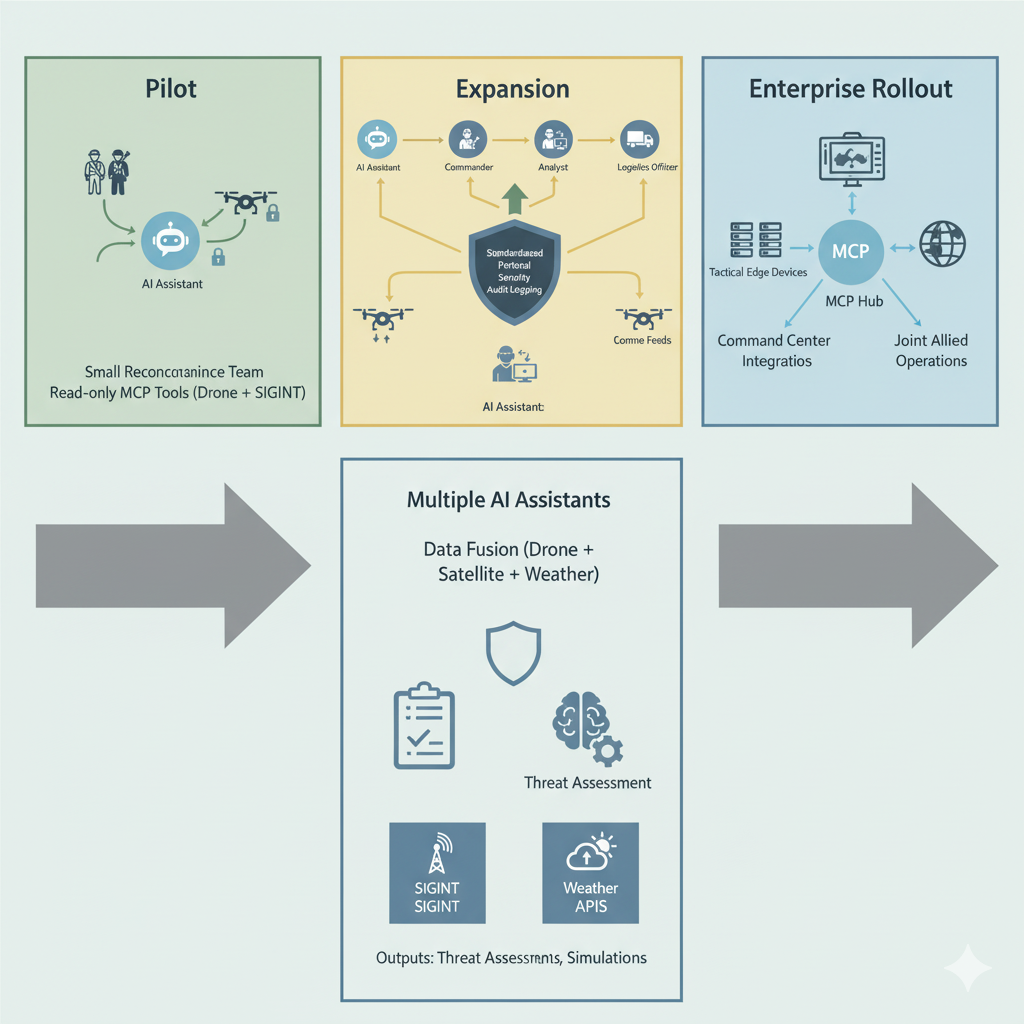
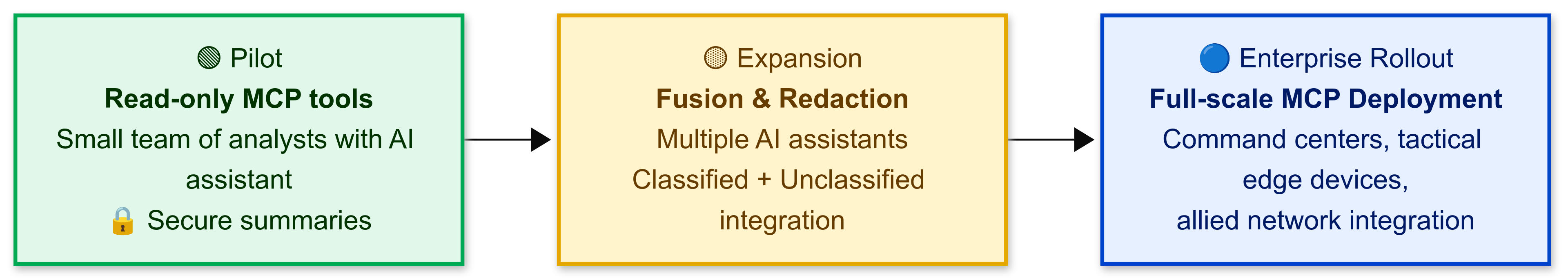
8. Phased Adoption Roadmap
| Phase | Focus | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 – Pilot | Read-Only Access | Wrap core DCGS and OSINT APIs as MCP tools; deploy to limited intelligence units. |
| Phase 2 – Expansion | Analytical Fusion | Add AI-driven correlation, secure reporting, and alert automation. |
| Phase 3 – Enterprise Rollout | Full Integration | Embed MCP across command systems, tactical edge devices, and allied networks. |
9. Measurable Benefits
| Metric | Before MCP | After MCP |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Complexity | High (custom integrations) | Low (standard MCP layer) |
| Time-to-Insight | 6–12 hrs | <1 hr |
| Compliance Violations | Risk-prone | Fully auditable |
| Operational Coverage | Siloed tools | Unified AI interface |
Tactical Advantages:
- Secure AI integration across classification levels
- Faster intelligence fusion and situational awareness
- Centralized governance and auditability
- Scalability across domains and allied networks
10. Lessons Learned
- MCP eliminates the need for brittle, point-to-point AI integrations.
- Attribute-based controls (ABAC) are critical for enforcing clearance boundaries.
- Redaction and sanitization pipelines enable safe, cross-domain knowledge sharing.
- Early pilots benefit from clear governance and HITL (human-in-the-loop) oversight.
11. Conclusion
By adopting the Model Context Protocol (MCP), defense agencies can unlock the power of AI copilots without compromising classified systems.
MCP acts as a secure, governed bridge between intelligence platforms and AI tools, enabling faster decision-making, mission agility, and compliance at every classification level.
Appendix: Implementation Checklist
- ✅ Wrap DCGS and ISR APIs as MCP tools
- ✅ Enforce OAuth 2.0 + Cross-Domain AuthN
- ✅ Define ABAC scopes per mission role (Analyst, Planner, Cyber Ops)
- ✅ Configure audit logs & automated redaction rules
- ✅ Begin with read-only → expand to analytical tools
- ✅ Embed MCP endpoints into command dashboards and tactical edge devices
Prepared by Frankmax Defense Intelligence – advancing secure, Responsible AI integration across mission-critical environments.